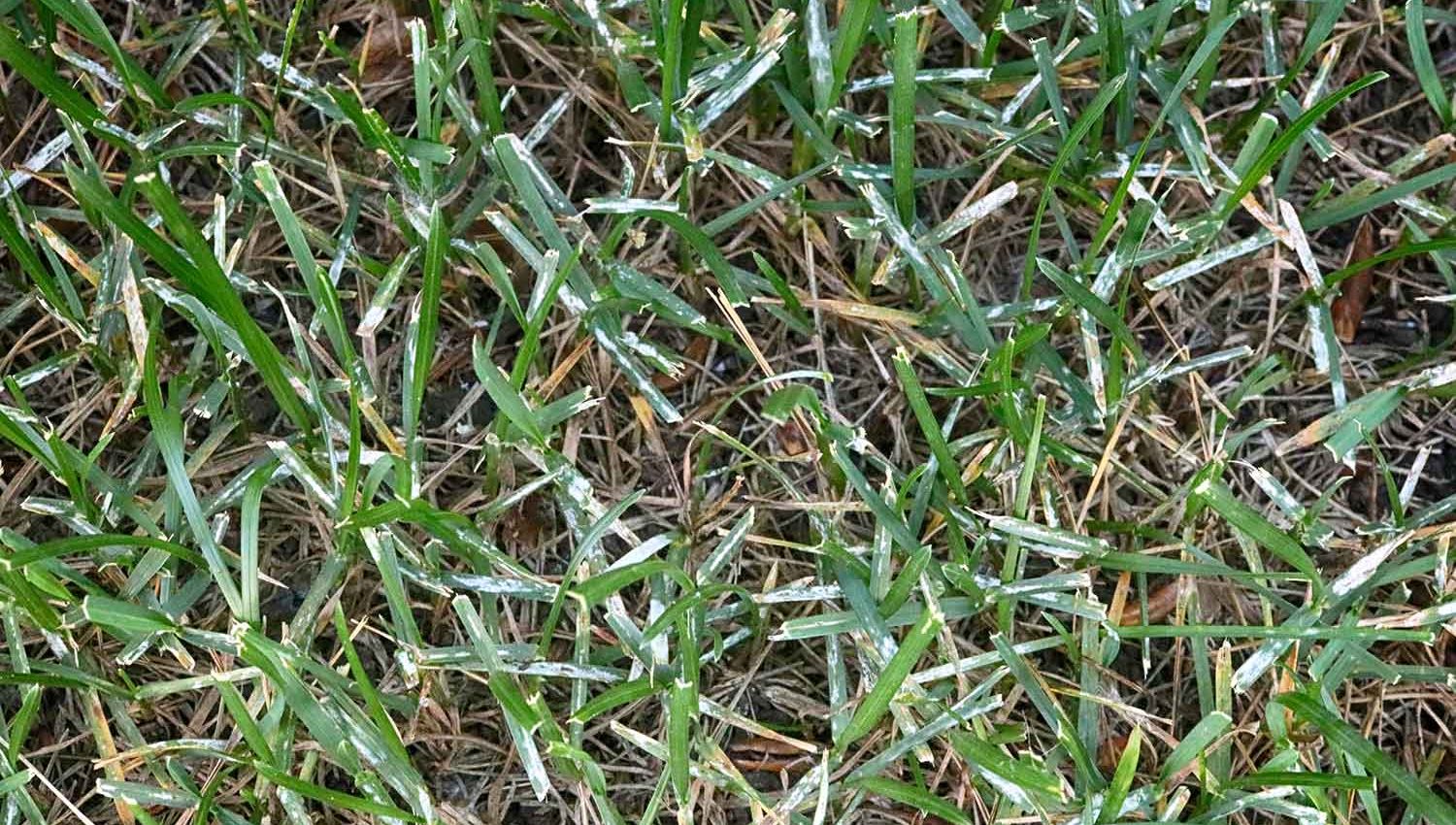
What Is Powdery Mildew

How To Prevent Powdery Mildew
As we well know, prevention is the goal when it comes to any sort of plant disease. With care and planning, there are several things you can do to prevent powdery mildew from forming on your plants, including:
Plant fungal-resistant varieties:
While there aren’t any plants immune to powdery mildew, there are many varieties of plants that are resistant to it. When choosing plants for your garden, be sure to select resistant varieties such as cantaloupe, cole crops, cucumber, melons, peas, pumpkins, and squash.
Water plants properly:
Water plants at the base of the stem rather than from overhead. This will help prevent the leaves from getting wet, creating an environment where powdery mildew can thrive.
Improve air circulation:
Powdery mildew is more likely to develop in areas with poor air circulation. Prune your plants to improve air circulation, and avoid planting them too close together.
Fertilize properly:
Over fertilizing plants with nitrogen can make them more susceptible to powdery mildew. Fertilize your plants according to the directions on the fertilizer label.
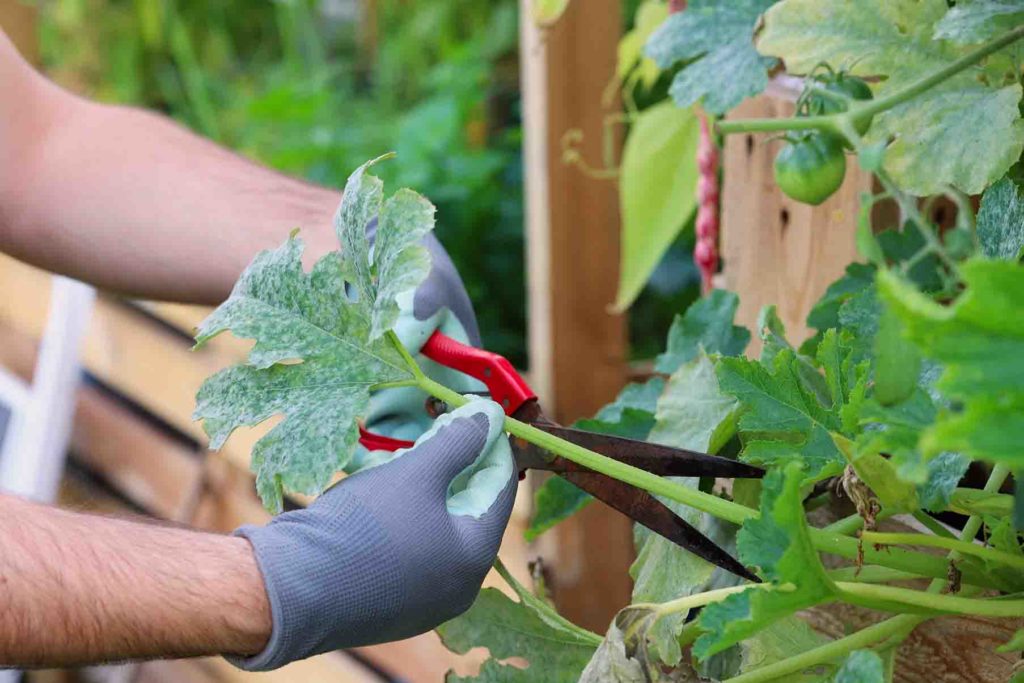
Remove infected leaves:
Remove the infected leaves immediately if you see powdery mildew on your plants. Do not compost the infected leaves, as this can spread the disease.
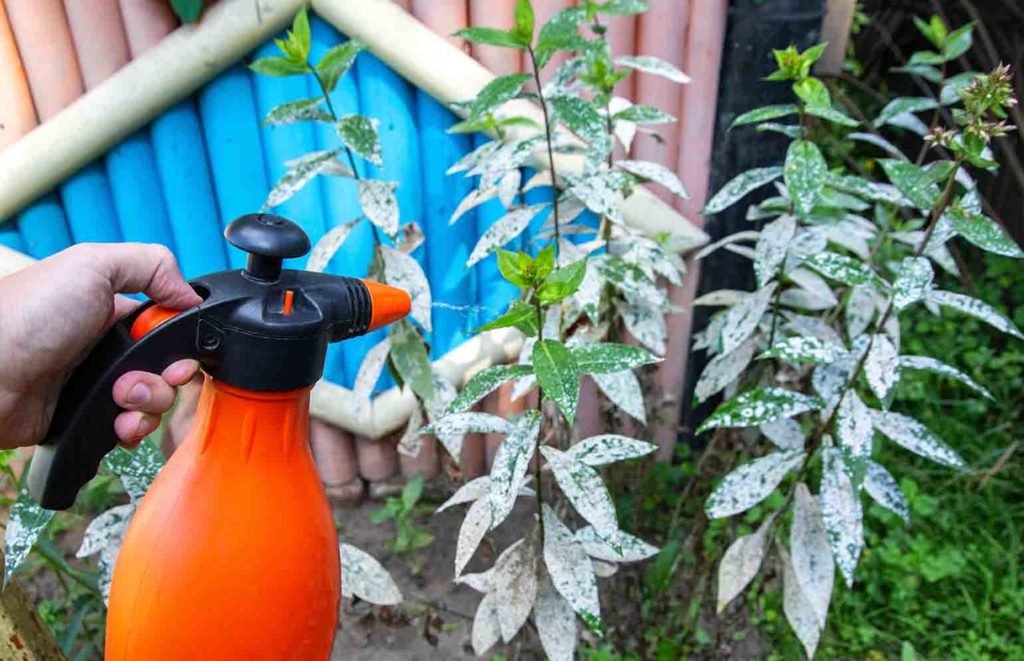

How To Treat Powdery Mildew
Fortunately, powdery mildew is common enough that there are many products on the market targeting to preventing and treating the disease. Many seasoned gardeners still use classic home remedies for their gardens to keep this fungal disease at bay. These remedies can be time-consuming, as they take multiple applications over several weeks time. Still, many gardeners and experts alike agree on the effectiveness of the tried and true methods listed below.
Baking soda solution:
1. Mix 1 tbsp of baking soda with ½ tsp of liquid soap (not detergent) in 1 gallon of water.
2. Spray the solution liberally on the plant’s affected areas, including the leaves’ top and bottom.
3. Repeat the application every 7-10 days until the powdery mildew is gone.
Potassium bicarbonate solution:
1. Mix 1 tbsp of potassium bicarbonate with ½ tsp of liquid soap (not detergent) in 1 gallon of water.
2. Spray the solution liberally on the plant’s affected areas, including the leaves’ top and bottom.
3. Repeat the application every 7-10 days until the powdery mildew is gone.
Milk Solution:
1. Mix 1 part milk with 2-3 parts water.
2. Spray the solution liberally on the plant’s affected areas, including the leaves’ top and bottom.
3. Repeat the application every 7-10 days until the powdery mildew is gone.
Neem oil solution:
1. Mix 1 tablespoon of neem oil with 1 gallon of water.
2. Add a few drops of dish soap to help the oil mix with the water.
3. Spray the solution liberally on the plant’s affected areas, including the leaves top and bottom.
4. Repeat the application every 7-10 days until the powdery mildew is gone.
Powdery mildew fungicide:
1. Follow the directions on the fungicide label.
2. Apply the fungicide as directed.
3. Repeat the application as needed to control the powdery mildew.
It is important to note that these treatments may only be effective on some plants. If you are unsure which treatment to use, your best bet is to consult with a gardening expert.
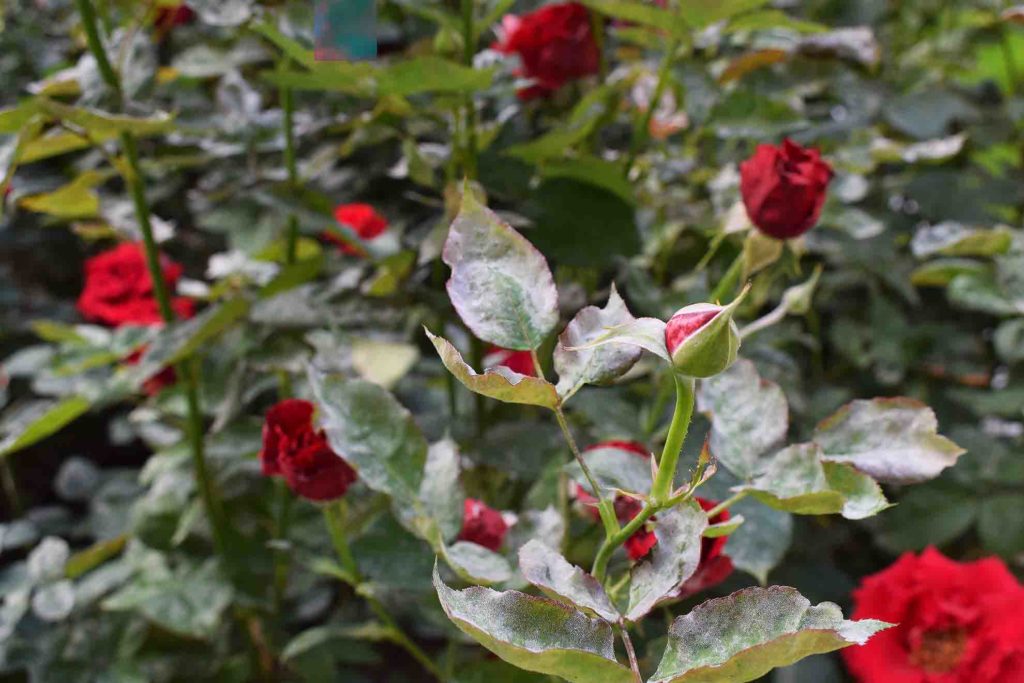

While all plants are at risk of developing powdery mildew, some plants are more susceptible than others. These plants must be watched closely and treated at the first sign of the fungus, as it can spread quickly.
- Begonias
- Sunflowers
- Chrysanthemums
- Dahlias
- Roses
- Zinnias
- Melons
- Zucchini
- Squash
- Lettuce
- Cucumbers
- Potatoes
- Parsley
- Pumpkins
- Grapes
- Peppers
- Tomatoes
Start Your Quote Today! Getting Started
Get your weekend back & simplify your life this season. Trust Elite Lawn Care for your Lawn Care, Landscaping & Snow Removal needs.
-
1Choose Your ServicesChoose the services your property needs throughout the year.
-
2Set Up & Finalize Your AccountFill out the form & one of our team members will contact you.
-
3Discover The DifferenceServices are automatically scheduled, completed & billed.